Breast cancer
Cancer - breast; Carcinoma - ductal; Carcinoma - lobular; DCIS; LCIS; HER2-positive breast cancer; ER-positive breast cancer; Ductal carcinoma in situ; Lobular carcinoma in situ
Breast cancer is cancer that starts in the tissues of the breast. There are two main types of breast cancer:
- Ductal carcinoma starts in the tubes (ducts) that carry milk from the breast to the nipple. Most breast cancers are of this type.
- Lobular carcinoma starts in the parts of the breast, called lobules, which produce milk.
In rare cases, other kinds of breast cancer can start in other areas of the breast.
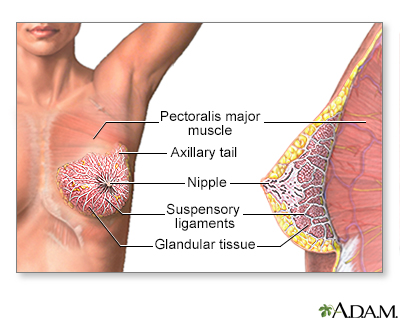
The female breast is either of two mammary glands (organs of milk secretion) on the chest.
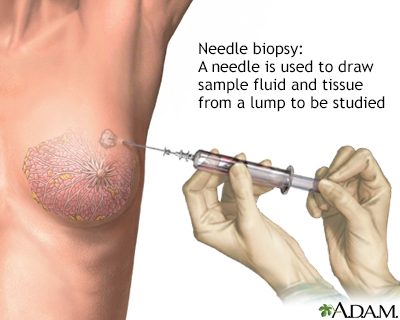
A needle biopsy is performed under local anesthesia. Simple aspirations are performed with a small gauge needle to attempt to draw fluid from lumps that are thought to be cysts. Fine needle biopsy uses a larger needle to make multiple passes through a lump, drawing out tissue and fluid. Withdrawn fluid and tissue is further evaluated to determine if there are cancerous cells present.
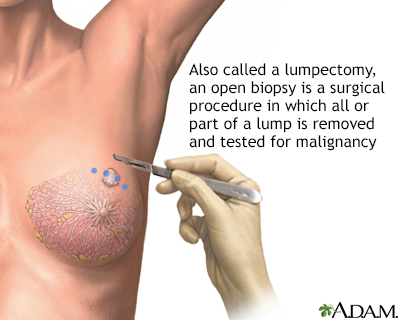
An open biopsy can be performed under local or general anesthesia and will leave a small scar. Prior to surgery, a radiologist often first marks the lump with a wire, making it easier for the surgeon to find.
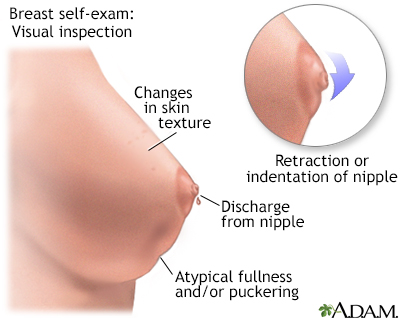
Monthly breast self-exams should always include a visual inspection, with and without a mirror, to note any changes in contour or texture, and manual inspection in standing and reclining positions to note any unusual lumps or thicknesses.
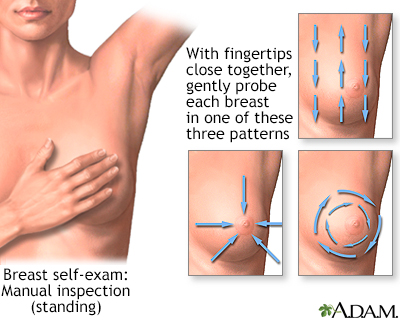
Monthly breast self-exams should always include a visual inspection, with and without a mirror, to note any changes in contour or texture, and manual inspection in standing and reclining positions to note any unusual lumps or thicknesses.
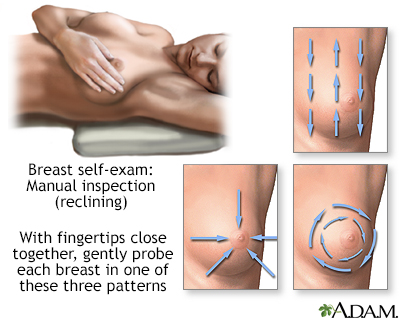
Monthly breast self-exams should always include a visual inspection, with and without a mirror, to note any changes in contour or texture, and manual inspection in standing and reclining positions to note any unusual lumps or thicknesses.
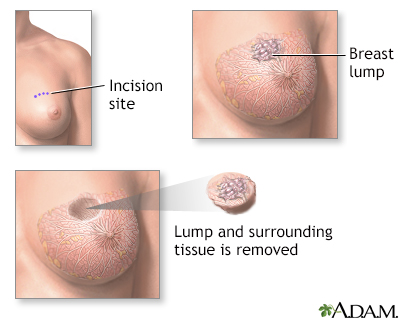
Lumpectomy is a surgical procedure performed on a solid breast mass to determine if it is malignant. The suspicious lump and some surrounding tissue is excised and analyzed.
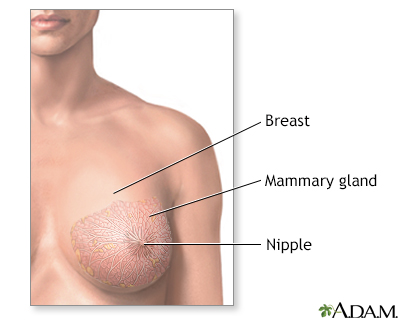
The female breast is composed mainly of fatty tissue interspersed with fibrous or connective tissue. The circular region around the nipple is often a different color or pigmented. This region is called the areola.
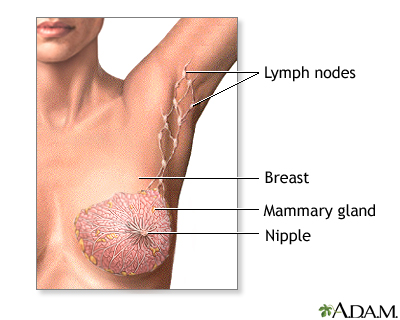
The female breast is composed mainly of fatty tissue interspersed with fibrous or connective tissue. The circular region around the nipple is often a different color or pigmented. This region is called the areola.
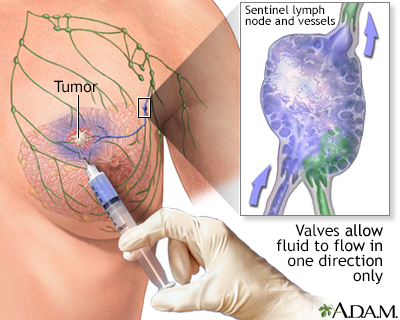
Sentinel node biopsy is a technique which helps determine if a cancer has spread (metastisized), or is contained locally. When a cancer has been detected, often the next step is to find the lymph node closest to the tumor site and retrieve it for analysis. The concept of the sentinel node, or the first node to drain the area of the cancer, allows a more accurate staging of the cancer, and leaves unaffected nodes behind to continue the important job of draining fluids. The procedure involves the injection of a dye (sometimes mildly radioactive) to pinpoint the lymph node which is closest to the cancer site. Sentinel node biopsy is used to stage many kinds of cancer, including lung and skin (melanoma).
Causes
Breast cancer risk factors are things that increase the chance that you could develop breast cancer:
- Some risk factors you can control, such as drinking alcohol. Others, such as family history, you cannot control.
- The more risk factors you have, the more your risk increases. But, it does not mean you will develop cancer. Most women who develop breast cancer do not have known risk factors or a family history.
- Understanding your risk factors can help you take steps to lower your risk.
Some women are at higher risk for breast cancer because of certain genetic changes or variants that may be passed down from their parents.
- Genes known as BRCA1 or BRCA2 are responsible for most cases of inherited breast cancers.
- A screening tool with questions about your family's history as well as yours can help your health care provider whether you are at risk for carrying these genes.
- If you are at high risk, due to a known abnormal gene such as BRCA1 or BRCA2, a blood test can show if you carry the genes.
- Certain other genes may lead to an increased risk of breast cancer.
Breast implants, using antiperspirants, and wearing underwire bras do not increase the risk for breast cancer. There is also no evidence of a direct link between breast cancer and pesticides.
Of all the different types of cancers, breast cancer is one of the most talked about, and with good reason. One out of every eight women will develop breast cancer sometime in their life. That's why every woman should be thinking about how to protect herself from this disease. Breast cancer is cancer that forms in the breast. Usually, it begins in the tubes that transport milk from the breast to the nipple. If the cancer spreads to other parts of the breast or body, it's called invasive breast cancer. Some breast cancers are more aggressive, growing more quickly than others. Although women are 100 times more likely to develop breast cancer, men can also get the disease because they do have breast tissue. You're more likely to get breast cancer if you're over 50, you started your periods before age 12, or you have a close family member with the disease. Drinking more than a couple of glasses of alcohol a day and using hormone replacement therapy for several years also may increase your risk. The telltale sign of breast cancer is a lump in your breast or armpit. You may also notice a change in the shape, size, or texture of your breast, or have fluid coming from your nipple when you're not breastfeeding. If you notice any changes in your breasts, call your doctor. You'll probably need to have an imaging scan, such as a mammogram, MRI, or ultrasound. A piece of tissue may be removed from your breast, called a biopsy. With these tests, your doctor can tell whether you have breast cancer, and if so, determine whether or not it has spread. So, how do we treat breast cancer? That really depends on the type of cancer, and how quickly it's spreading. Your doctor may recommend that you have the cancer removed with surgery. Sometimes it's enough just to remove the lump. That's called a lumpectomy. In other cases, the doctor will need to remove the entire breast to get rid of all the cancer or prevent it from coming back. That's called a mastectomy. Other treatments for breast cancer include chemotherapy, medicines that kill cancer cells, and radiation therapy, which uses energy to destroy cancer. Women whose cancer is fueled by the hormone estrogen may receive hormone therapy to block the effects of estrogen on their cancer. Today's breast cancer treatments are better than ever. Many women who have breast cancer go on to live long, healthy lives. The outlook really depends on how fast the tumor is growing, and how far it has spread. That's why it's so important to report any changes in your breasts to your doctor as soon as you notice them. Women who are at an especially high risk for breast cancer because of their family history can talk to their doctor about taking medicine or even having surgery to reduce their risk.
Symptoms
Early breast cancer often does not cause symptoms. This is why regular breast exams and mammograms are important, so cancers that don't have symptoms may be found earlier.
As the cancer grows, symptoms may include:
- Breast lump or lump in the armpit that is hard, has uneven edges, and usually does not hurt.
- Change in the size, shape, or feel of the breast or nipple. For example, you may have redness, dimpling, or puckering that looks like the skin of an orange.
- Fluid from the nipple. Fluid may be bloody, clear to yellow, green, or look like pus.
In men, breast cancer symptoms include breast lump and breast pain and tenderness.
Symptoms of advanced breast cancer may include:
- Bone pain
- Shortness of breath
- Swelling of the lymph nodes in the armpit (next to the breast with cancer)
- Weight loss
Exams and Tests
The provider will ask about your symptoms and risk factors. Then they will perform a physical exam. The exam includes both breasts, armpits, and the neck and chest area.
Women are encouraged to perform breast self-exams each month. However, the effectiveness of self-exams for detecting breast cancer is debatable.
Tests used to diagnose and monitor people with a breast lump or breast cancer may include:
- Mammography to screen for breast cancer or help identify a breast lump
- Breast ultrasound to show whether a lump is solid or fluid-filled
- Breast MRI to help better identify a breast lump or evaluate an abnormal change on a mammogram
- Breast biopsy, using methods such as needle aspiration, ultrasound-guided, stereotactic, or open
- Sentinel lymph node biopsy to check if the cancer has spread to the lymph nodes
- CT scan to check if the cancer has spread outside the breast
- PET scan to check if the cancer has spread outside the breast
If your provider learns that you do have breast cancer, more tests will be done. This is called staging, which checks if the cancer has spread. Staging helps guide treatment and follow-up. It also gives you an idea of what to expect in the future.
Breast cancer stages range from 0 to IV. The higher the stage, the more advanced the cancer.
If you're a woman, your doctor or gynecologist may have recommended that you examine your breasts every month to check for lumps. You might be wondering, why do I need to do a breast self-exam? Or, you might ask, how do I examine my breasts, and what exactly am I looking for? Well, let's talk about why, and how to examine your breasts. Why examine your breasts? Well, for one thing, it helps you get an idea of how they normally feel. Then if there's ever a problem, you'll be familiar enough with your breasts to spot it. For example, a lump on your breast could be a sign of breast cancer. Finding that lump could allow you to get checked out with a mammogram earlier than you might have done if you didn't do breast self exams. But, this is a two edged sword. Many expert groups no longer recommend routine breast self examination because the consequences of over treatment of benign or normal lumps may outweigh the benefits of early detection. Lumps lead to extra mammograms, which often lead to biopsies, and the biopsies turn out to be benign, or normal, in more than 90% of cases. But, not always. Some expert groups simply recommend breast self awareness. Ultimately, the choice is yours. If you are going to do breast self exam, the best day to do a self exam is about 3 to 5 days after your period ends. Your breasts are naturally less lumpy right after your period, so there's less of a chance that you'll mistake a normal bump for an abnormal growth. If you've already gone through menopause and your periods have stopped, just do your exam on the same day every month. Mark it on your calendar so you won't forget. To do the exam, lie on your back, as it's easier to feel any lumps or changes when you're lying down. First, put your right hand behind your head. Then, using the middle fingers on your left hand, gently but firmly press down, circling your entire breast. Make sure you cover the whole right breast. Squeeze your nipple gently. See if any fluid comes out. Now, sit up, and feel around your armpit. When you're done with the right breast, repeat the whole check on the left side. Next, stand in front of a mirror. With your arms down at your sides, look at both breasts. Check the shape of each breast. Look for any changes in the skin, like dimpling or puckering. Also see if your nipples now turn inward. Now, do the exact same check again with your arms over your head. After you've done a few breast self-exams, you'll become familiar with the look and shape of your breasts. At each exam, you're looking for anything different, like new bumps, changes in the texture of your skin, or discharge from your nipple. If you do notice that something has changed, don't panic, it could mean many different things. But, call your doctor as soon as you can so you can find out what's caused the change, and, if necessary, get it treated.
Treatment
Treatment is based on many factors, including:
- Type of breast cancer
- Stage of the cancer (staging is a tool your providers use to find out how advanced the cancer is)
- Whether the cancer is sensitive to certain hormones
- Whether the cancer overproduces (overexpresses) the HER2/neu protein
- Tests on the tumor's genes to see if you would benefit from chemotherapy
Cancer treatments may include:
- Hormone therapy.
- Chemotherapy, which uses medicines to kill cancer cells.
- Radiation therapy, which is used to destroy cancerous tissue.
- Surgery to remove cancerous tissue: A lumpectomy removes the breast lump. Mastectomy removes all or part of the breast and possibly nearby structures. Nearby lymph nodes may also be removed during surgery.
- Targeted therapy uses medicine to attack the gene changes in cancer cells. Hormone therapy is an example of targeted therapy. It blocks certain hormones that fuel cancer growth.
Cancer treatment can be local or systemic:
- Local treatments involve only the area of disease. Radiation and surgery are forms of local treatment. They are most effective when the cancer has not spread outside the breast.
- Systemic treatments affect the entire body. Chemotherapy and hormonal therapy are types of systemic treatment.
Most women receive a combination of treatments. For women with stage I, II, or III breast cancer, the main goal is to treat the cancer and prevent it from returning (recurring). For women with stage IV cancer, the goal is to improve symptoms and help them live longer. In most cases, stage IV breast cancer cannot be cured.
- Stage 0 (for example, ductal carcinoma in-situ) and ductal carcinoma: Lumpectomy plus radiation or mastectomy is the standard treatment.
- Stage I and II: Lumpectomy plus radiation or mastectomy with lymph node removal is the standard treatment. Chemotherapy, hormonal therapy, and other targeted therapy may also be used after surgery.
- Stage III: Treatment involves surgery, possibly preceded or followed by chemotherapy, hormone therapy, and other targeted therapy.
- Stage IV: Treatment may involve surgery, radiation, chemotherapy, hormone therapy, other targeted therapy, or a combination of these treatments.
After treatment, some women continue to take medicines for some time, often several years. All women continue to have mammograms to monitor for the return of cancer or development of another breast cancer.
Women who have had a mastectomy may have reconstructive breast surgery. This will be done either at the time of mastectomy or later.
Support Groups
You can ease the stress of illness by joining a cancer support group. Sharing with others who have common experiences and problems can help you not feel alone.
Outlook (Prognosis)
New, improved treatments are helping people with breast cancer live longer. Even with treatment, breast cancer can spread to other parts of the body. Sometimes, breast cancer returns, even after the entire tumor has been removed and nearby lymph nodes are found to be cancer-free.
Some women who have had breast cancer develop a new breast cancer that is not related to the original tumor.
How well you do after being treated for breast cancer depends on many things. The more advanced your cancer, the poorer the outcome. Other factors that determine the risk for recurrence and the likelihood of successful treatment include:
- Location of the tumor and how far it has spread
- Whether the tumor is hormone receptor-positive or -negative
- Gene expression
- Tumor size and shape
After considering all of the above, your provider can discuss your risk of having a recurrence of breast cancer.
Possible Complications
You may experience side effects or complications from cancer treatment. These may include temporary pain or swelling of the breast and surrounding area. Ask your provider about the possible side effects from treatment.
When to Contact a Medical Professional
Contact your provider if:
- You have a breast or armpit lump
- You have nipple discharge
After being treated for breast cancer, call your provider if you develop symptoms such as:
- Nipple discharge
- Rash on the breast
- New lumps in the breast
- Swelling in the area
- Pain, especially chest pain, abdominal pain, or bone pain
Prevention
Talk to your provider about how often you should have a mammogram or other tests to screen for breast cancer. Early breast cancers found by a mammogram have a good chance of being cured.
Tamoxifen is approved for breast cancer prevention in women age 35 and older who are at high risk. Discuss this with your provider.
Women at very high risk for breast cancer may consider preventive (prophylactic) mastectomy. This is surgery to remove the breasts before breast cancer is diagnosed. Possible candidates include:
- Women who have already had one breast removed due to cancer
- Women with a strong family history of breast cancer
- Women with genes or genetic mutations that raise their risk for breast cancer (such as BRCA1 or BRCA2)
Many risk factors, such as your genes and family history, cannot be controlled. But making healthy lifestyle changes may reduce your overall chance of getting cancer. This includes:
- Eating healthy foods
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Limiting alcohol consumption to 1 drink per day
References
Harnden K, Mauro L, Pennisi A. Breast cancer. In: Ginsburg GS, Willard HF, Strickler JH, McKinney MS, eds. Genomic and Precision Medicine: Oncology. 3rd ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2022:chap 9.
Makhoul I. Therapeutic strategies for breast cancer. In: Bland KI, Copeland EM, Klimberg VS, Gradishar WJ, eds. The Breast: Comprehensive Management of Benign and Malignant Diseases. 5th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier; 2018:chap 24.
National Cancer Institute website. Breast cancer treatment (adult) (PDQ) - health professional version.
National Comprehensive Cancer Network website. NCCN clinical practice guidelines in oncology (NCCN guidelines): Breast cancer. Version 3.2022.
Siu AL; US Preventive Services Task Force. Screening for breast cancer: US Preventive Services Task Force recommendation statement. Ann Intern Med. 2016;164(4):279-296. PMID: 26757170
US Preventive Services Task Force, Owens DK, Davidson KW, et al. Risk assessment, genetic counseling, and genetic testing for BRCA-related cancer: US Preventive Services Task Force Recommendation Statement [published correction appears in JAMA. 2019;322(18):1830]. JAMA. 2019;322(7):652-665. PMID: 31429903
Version Info
Last reviewed on: 2/2/2023
Reviewed by: Mark Levin, MD, Hematologist and Oncologist, Monsey, NY. Review provided by VeriMed Healthcare Network. Also reviewed by David C. Dugdale, MD, Medical Director, Brenda Conaway, Editorial Director, and the A.D.A.M. Editorial team. Editorial update 06/05/2023.
